이번 글에서는 gene regulation 중 Transcriptional control에 대해 전 글에 이어 작성해보도록 하겠습니다.
[10일차] Transcriptional Factors에 의한 gene regulation, Transcriptional Activation
Bacterial Operon에 이어 이번엔 Eukaryotes의 gene expression 조절 기전에 대해 살펴보도록 하겠습니다. [10일차] Lac Operon(structural genes, promoter, operator), 그리고 lactose와 관련된 β-galactosidase 등의 효소오늘은
tkmstudy.tistory.com
먼저 Transcriptional control 과정 중 Transcriptional repression 과정인 Histone methylation에 대해 정리해보겠습니다.
Histone methylation은 히스톤의 아미노산에 methyl groups를 전달하는 과정으로, 이를 통해 chromatin을 활성화하거나 비활성화하도록 histones를 변화시킨다고 하며,
대부분의 methlyation은 DNA를 turn off, demethylation은 turn on하며, 이는 transcription factors를 DNA에 붙지 못하게 하거나 붙지 못하도록 함으로써 조절한다1)고 합니다.
아래 영상에서 Histone Methlyation에 대해 소개해주고 있는데, 반응이 일어나는 맥락(위치)에 따라 methylation이 전사의 억제가 아닌 활성을 유도할 수 있는 듯 합니다.
특히 histone-DNA interaction을 약하게 하여 transcription activation을 야기하는 histone acetylation과 달리, histone methylation은 histons의 basicity(염기성)와 hydrophobicity(소수성)을 증가시켜 DNA-transcription factors interaction에 영향을 주어 gene expression을 활성화하거나 억제한다2)고 하죠.
이러한 Histone methylation은 DNA repair, cell cycle, stress respone, development를 위한 transcription, differentiation, ageing 등 모든 생물학적 과정에 관여하며, 그럼으로서 개체의 수명(longevity)을 regulate한다고 밝혀졌다3)고 합니다. 한마디로 굉장히 중요한 후성유전학적 과정입니다.
본 과정에서 methyl groups를 histon tails로 전달하는건 writers의 역할을 하는 histone methyl-transferases (HMTs)가 담당하며, 이후엔 readers가 methyl groups를 인식하여 결합하여 gene expression에 영향을 미칩니다.
histon demethylases(HDMs)라는 erasers도 있는데, 이 효소는 methyl groups를 제거합니다. 종합적으로 HMTs와 HDMs이라는 효소들이 함께 nucleosome의 histone methylation level을 조절함2)으로써 gene expression pattern을 결정합니다.
아래는 histone에 acetyl group이 사라지고 methyl groups이 더해져 chromatin inactivation과 gene silencing이 유도되는 transcriptional repression 과정을 이미지로 나타낸 것입니다.
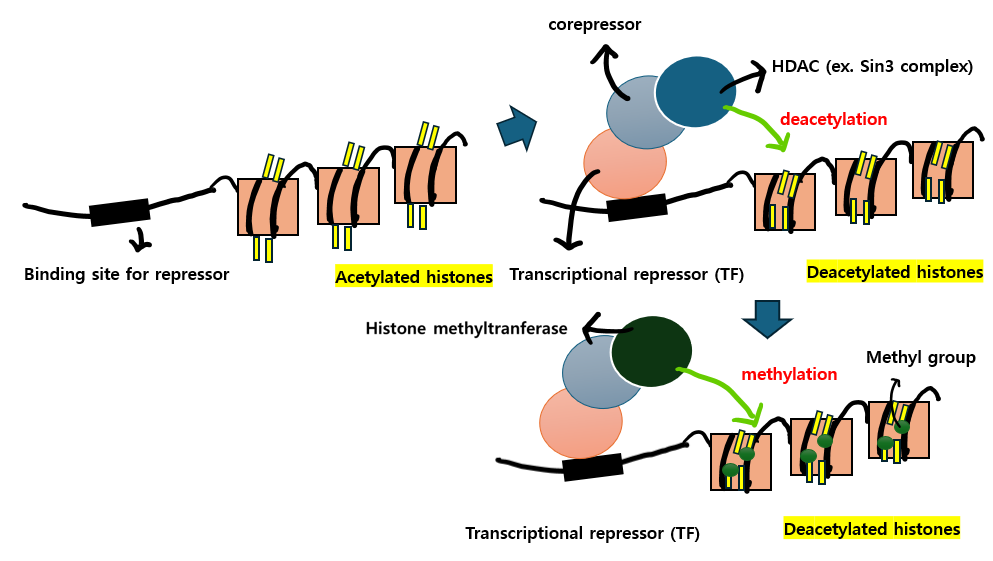
Histone methylation이 DNA methylation patterns에 직접적으로 도움을 주는 과정이었다면, DNA methlyation은 DNA replication 후에 histone modification patterns의 rebuilding을 위한 template으로서 long-term stability를 위한 역할4)을 합니다.
DNA methylation에서는 DNA-methyl-tranferases가 역할을 하며, DNA methylation과 histone modification의 관계를 이해하는 것은 tumorigensis와 somatic cell reprogramming 뿐만 아니라 normal development를 이해하는데에도 적용할 수 있다4)고 하네요. DNA methylation에 대한 설명은 아래 영상을 참고하시면 될 것 같습니다.
특히, DNA methylation은 gene이 inactive state로 유지될 수 있게 하여 불필요한 증식이 이루어지지 않도록 하는데, 예로 증식이 필요한 zygote가 되는 과정에선 demethylation(DNA가 methylation tag를 잃음), 그리고 embryo가 adult somatic cells가 되는 과정에선 methylation이 유지됩니다.
또한, methylation patterns의 차이는 imprinted genes의 활성과 비활성을 결정하며 잘못되면 human genetic disorders가 발생할 수 있습니다. 참고로 genomic imprinting은 엄마에게 받은 유전자와 아빠에게 받은 유전자인지에 따라 다르게 발현되는 현상 5)으로 DNA methylation을 통해 어떤 유전자의 형질이 발현될지 결정됩니다.
아래 영상을 보시면 genomic imprinting에 대해 이해하실 수 있을텐데, methylation에 대한 설명과 겹치는 부분이 있는 듯 합니다.
참고로 Long nodoing RNAs (lncRNA)는 이러한 메틸화 과정을 이용해 Transcriptional Repression을 위한 repressors로서 역할을 할 수 있습니다.
예로, 사람의 early embryo의 anterior-posterior axis를 결정하는 HOX genes의 lncRNA 'HOTAIR'는 PRC(histone methyltransferase)와 상호작용하는 5' end와 CoREST(histone demethyltransferase)가 결합하는 3'end를 갖습니다. 이때 PRC의 HSK27 메틸화는 HOX gene의 특정 loci에 있는 chromation의 transcriptionally inactive state를 유도하고, CoREST는 메틸화된 H3K4(transcriptionally active genes)의 methyl group을 제거해 demethylation시켜 transcirptional repression을 유도합니다. 앞서 말했듯 DNA의 위치와 맥락에 따라 methylation이 전사를 억제할수도 활성화할 수도 있습니다.
지금까지 methylation에 대해 간단하게 알아보았는데, methylation이 전사 과정을 조절하는 과정에 대한 설명은 자세히 다루지 못한 만큼 나중에 관련 논문을 읽어보아야겠습니다.
이것으로 Transcriptional Control을 마치고, 다음 글에선 RNA processing control, 그리고 translational control에 대해 다뤄보도록 하겠습니다.
참고자료
1) Michel Neidhart, in DNA Methylation and Complex Human Disease, 2016
2) CUSAIBO, Histone Methylation, URL : https://www.cusabio.com/histones/histone-methylation.html
3) Greer, E., Shi, Y. Histone methylation: a dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat Rev Genet 13, 343–357 (2012).
4) Cedar, H., Bergman, Y. Linking DNA methylation and histone modification: patterns and paradigms. Nat Rev Genet 10, 295–304 (2009).
5) NAVER 지식백과, 유전체 각인
유전체 각인
멘델의 유전법칙을 따르지 않는 독립적인 유전 형태로, 특정 유전 형질이 부모 중 누구에게서 유래되었는지에 따라 다르게 나타나는 후성적인 현상이다. 인간과 같은 이배체 유기체의 체세포에
terms.naver.com




